SEO Philippines Services
Powered by Data for Growth
Our experts at our SEO agency in the Philippines determine the optimal content and keyword strategy to get the best results possible. And we explain our thinking every step of the way.

Don't simply take our word for it. Check out what some of our clients have to say about Spiralytics:
4.5 Star Ratings Globally





















Trusted by Leading Brands to Drive Growth
with Targeted Digital Strategies

















SEO in the Philippines
for the World
With about 5.16 billion internet users worldwide today, search engine optimization (SEO) has become more critical than ever if you want your website to perform well. Partnering with an SEO company in the Philippines, like Spiralytics, can help you achieve that.
The Philippines is known for its tech-savvy and digitally proficient workforce. The country’s internet users spend an average of 9.14 hours browsing the net, making SEO Philippines a hub of expertise. As such, Filipinos have developed a deep understanding of the online space.
Our professional SEO services can enhance your website’s performance regardless of where your business is based. Equipped with expert knowledge and proper SEO tools, we can help boost your brand’s online visibility and increase traffic for more conversion opportunities.

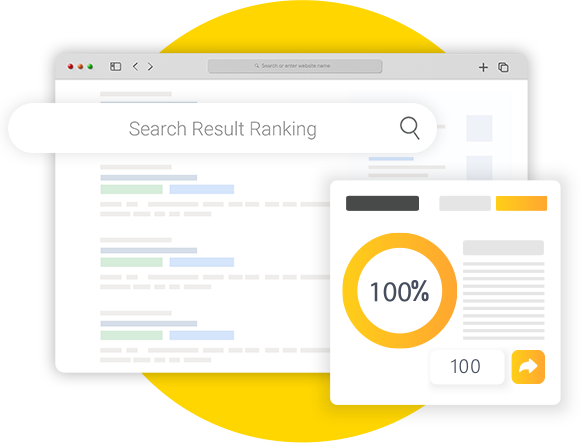
Achieved Record-High
218% Organic Traffic Growth with Spiralytics
beBOLD Digital struggled to find the right keywords for their website, resulting in low organic traffic and limited visibility on key pages.
Here’s how Spiralytics’ efforts helped improved their website quality.

SEO Campaigns fail for the following reasons:

SEO companies or SEO consultants don’t collaborate to understand your business and how your ideal future customers search for you

A strong content strategy is not implemented to build authority across your entire site

Target landing pages are not methodically improved to clearly explain your service, educate your future customers and keep them on your site for conversion or lead generation

The right metrics aren’t tracked to ensure success
As a dedicated SEO agency, we’re here to understand your business, competitors, focus products, and requirements. This allows us to tailor our organic marketing services and show you exactly how we plan to get results with our SEO strategies.
Click on the “Get a Quote” button below and we’ll set up a quick call with you!
Our Approach
Search ads can be a great way to drive new business profitably, but 95% of searchers skip the ads and go directly to the regular, non-paid organic search results. Your business needs to be there, as many people associate Google’s trust in your website as a business they’d like to work with.
Our approach looks like this:

Prioritize Your Products & Services

Keyword Research

On-page Optimization

Content Strategy & Outreach Link-building Campaign

Technical Audit & Improvement Plan

Report on Progress, Continuously Improve
Our professional SEO services approach works
for all types of businesses:

B2B Lead Generation
This approach tends to be a “needle in the haystack” where your target market is small, but your average revenue per client is large. Oftentimes, potential clients use Google to build up their target list for RFP, and your company needs to be on page 1.

B2C Lead Generation
We’ve done extensive work here as well. Your site is used to generate leads, and then pass those leads to a sales team to close the business. Similar to B2B, we are constantly in contact with your sales team to let us understand the quality of leads and the leads that convert to sales. We optimize our efforts to the best performing keywords and pages on your site.

eCommerce or SaaS
The approach for eCommerce sites is similar to B2C lead generation, except that the website is where the sales transaction occurs. Oftentimes, the volume of products and categories is quite large, and we need to focus on the top performing categories initially, then work our way out to the rest of the site. We implement a tight feedback look with analytics and your historical sales to help make these decisions. Also, price wars lead to rapid changes in conversion rates if you have competitors selling the same or similar products.

Publishers
Publishers typically make money on placements, through both native articles and pay per click. SEO Organic traffic is critical. Similar to our Blog Optimization Process, we have built a tool that systematically reviews each page of your site (even if there are thousands), and looks for keyword opportunities.
What it's like to
Work with Spiralytics

We Launch Quickly!
Most other agencies claim that they need 1 month of R&D before they can launch. This is wasteful as many things can be implemented in the first week:
- Setting up Google Analytics (accurate tracking, conversions)
- Setting up Google Search Console
- Keyword Research for the first 10 pages for your review
- On-Page Optimization for the first 10 pages
- Initial SEO Technical Audit
- Initial Content ideas to earn links
Start Your SEO Service Journey Today!
Help your business find success in the digital space with a leading SEO company in the Philippines. You can easily make it happen through our organic marketing services and tailored SEO strategies.
More and more people are now using the internet. A broad untapped market is waiting to be introduced to your brand! The growing number of users makes implementing SEO all the more important to your marketing strategy.
Are you new to SEO but interested to see how your business can benefit from it?
Leveraging the Power of SEO for Businesses Online
Every business aims for an ROI that’s both measurable and significant. Many are skeptical of using SEO services in the Philippines because it takes time before the hard work pays off. Thus, they feel SEO isn’t significant to their company’s growth or that it’s a low-priority strategy.
Some businesses also think SEO is too technical to learn. Cost is also a factor for general hesitancy since you’ll need financial resources to avail good-quality content and perform SEO-related processes.
At Spiralytics, we will take care of your SEO needs so you can stop worrying and start focusing on growing your business.
Choosing the Right SEO Service for Your Business
Digital marketing agencies have sprouted in the country, with most offering SEO packages one way or another. Depending on the SEO company in the Philippines you choose, you’re in for a unique experience.
At Spiralytics, we offer professional SEO services that can help all types of businesses. We offer several SEO packages, including affordable SEO in the Philippines and other countries like the US, UK, Australia, and more. Our SEO services range from page optimization and keyword research to link building and SEO audit, all with reliable turn-around times and a collection of satisfied clients.
Prioritize Your Products & Services
Our SEO team will analyze each target page:
- List out all ranking and non-ranking relevant keywords
- Search volumes
- Keyword difficulty
Based on your site’s authority we’ll show you the opportunities for fastest gains. We then collaborate with you to finalize the prioritization that will work for your unique business:
- Profitability
- Highest close rates of sales qualified leads (or eCommerce conversion rates)
- Strategic Products & Initiatives
Keyword Research
What searches are most relevant for people looking for your business
We start by learning as much as we can about your products, services, and the target market for each. By focusing on your best customers, we reverse engineer to understand how they would search online when looking for you. Our competitor benchmarking strategies can help us see what your competitors are doing and how you fare against the competition in terms of keywords and ranking.
We then look at the following to determine where to focus:
- Results of ad spend for those keywords (if you have a PPC campaign running)
- Monthly search volume in your target market
- Relevancy to determine conversion-focused keywords versus informational searches
- Difficulty to avoid challenging searches until you’ve built up authority in Google’s eyes
SEO On-page Optimization
Once this analysis is complete, we tune each page of your site to rank for our target keywords. We choose which keywords to focus on for a particular page, and then optimize the following page elements:
- Title, Description, Headlines,
- Content,
- Internal & External Links
- Schema
- Speed & Core Vitals
When the page is tuned, we focus on improving click-through rates of your page. We run experiments to encourage more people to click through to your site, and at the same time, make the page more appealing so that future customers stay on your page longer.

Content Strategy & Outreach Link Building (aka “Online PR”)
In parallel with Keyword Research and On-Page Optimization, we need to build up the authority of your site in Google’s eyes. Content that helps your future customers succeed is the core of great SEO results.
The best links are earned by content that provides value to your future customers. Our Content Marketing Services are specifically designed to build content that earns links.
We also pay very close attention to content types that earn links naturally, without outreach. Tuning your content for this is the way to truly scale authority-building for your site.
The team is also highly experienced in finding other creative ways of encouraging other site owners, bloggers and journalists to link to your site:
-
HARO
(Help a Reporter Out). We scour this site to look for opportunities where you can be an expert reference. -
Guest Posting
We pitch stories to different sites for guest posting spots. -
Mentions
We have tools to pick up all mentions of your brand and business online, and then reach out to owners of these sites for link building opportunities or online reputation management. -
Broken Link Building
We reach out to sites with broken links to let them know about the missing content and offer similar content on your site. -
Stolen Images and Content
We have tools to detect when your custom images and content are used without proper attribution. We reach out to the person who used your intellectual property, and request attribution (a link!) to your website. -
Industry News
If your blog is first to cover breaking industry news, journalists will be quick to reference your post. -
Other Techniques
As we benchmark your competitors and uncover the best performing content in the industry, we’ll often find unique tactics that acquire links.
Technical SEO Audits
We will perform an initial audit upon launch, and then monthly maintenance checks to make sure nothing is broken as you are adding new content to your site:
-
Page speed
This is critical to Google, as well as your website visitors. Slow loading increases bounce rate and decreases conversions. -
Robots.txt & Sitemap
These tools ensure that Google’s crawlers visit your priority pages as frequently as possible, and ignore non-critical pages. We check that all of your priority pages are in the sitemap, and that all of them are indexed. -
Broken Links
If you delete content on your site and other pages are linking to it, you need to update those links. Not doing so provides bad user experience, as most people leave a site when they experience your “404 page”. -
Duplicate Content
Sometimes your content management system will unknowingly create duplicate pages across your site or duplicate tags. We scan for this and correct it as it happens. Too much of this can encourage Google to reduce the visibility of your site. -
Mobile Usability
In 2018, Google introduced this as a negative ranking factor. We’ve built a tool to find cases where your site ranks differently on desktop than it does on mobile, and highlights it as a potential issue. -
Core Web Vitals
This is a new metric Google has introduced to estimate user experience problems. If your page is difficult to use, Google will deprioritize you in the rankings.
Before we start all of our SEO optimization work, we highly advise to take a good look identifying weak spots in your website preventing conversions. This is called Conversion Rate Optimization. We look at 3 aspects of your site to look for common problems:

HotJar
This is a heatmap tool that shows where visitors click and hover on each page, shows scroll depth, and records visitor sessions to highlight problems.

Heuristic Best Practices
Best practices such as trust symbols near calls-to-action can easily be overlooked. We have a checklist of 50 common problems that we audit to identify improvement areas. After looking at each of the above 3, we create a series of A/B tests that we believe will improve the conversion rate of your site. We show you the rationale behind each, and then you decide if you’d like us to implement these tests.

Analytics
Google Analytics can show you pages that have unreasonable bounce rates, lack of conversion, and exit rates. We walk through a standard audit and uncover problem areas.
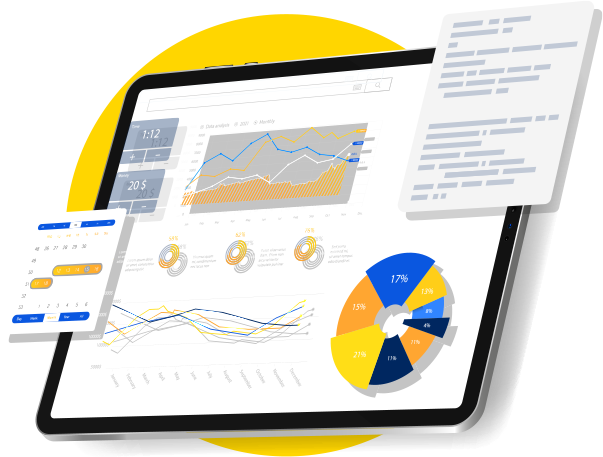
Fully Automated Reporting
Most digital marketing agencies report monthly on SEO. Our automated platform allows you to see results in real time
- Inquiries and Conversions from SEO, and which pages delivered
- Traffic Improvement by page, or grouped by different parts of your site
- Keyword Rankings
- Keyword Opportunities
- Links
As we build your organic traffic and add new powerful links, our team will give you insights into the reasons for improvement and offer new ideas that we are discovering as we move through our optimization process. Since reporting is automated, there is no “doctoring” of the results each month. The data is transparent, and you have full access for free as part of each SEO implementation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Search Engine Optimization
What is SEO and how does it work?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It’s the process of optimizing your website to drive organic traffic for search engines like Google and Bing. This means tweaking various elements of your site to make it more “attractive” to search engines. The end goal of SEO is to rank high on results pages when users search using keywords related to your website.
How long does it take to rank on SERPs?
The answer depends because there are many factors to consider: budget, website age/strength, competition, etc. Generally, it takes 3-6 months to see dramatic results, but only if you do it right. This isn’t so bad considering the average result on page one is more than 2 years old, while those that rank #1 are roughly 3 years old on average.
Credible, truthful, relevant, and engaging content could turn what would otherwise be a disadvantage into a very efficient and speedy “sales call.”
What are the most important SEO ranking factors?
Google utilizes more than 200 ranking factors in their algorithm, which makes it all the more necessary to work with a knowledgeable SEO team to help you rank on the search results. Some of the most crucial ranking factors are:
- Backlink profile
- Social signals
- Mobile-friendliness
- Content quality
- Page speed
- Optimized media (images + video)
- User Experience (UX)
How can you get penalized by Google?
Google penalizes websites if they fail to abide by their Webmaster Guidelines. SEO strategies that engage in illicit practices or suspicious behavior to manipulate the rankings can result in a Google penalty. When this happens, the site can either drop in rankings for a specific keyword or disappear on the SERPs altogether. Getting penalized can negatively affect a brand’s visibility, traffic, and revenue.
Credible, truthful, relevant, and engaging content could turn what would otherwise be a disadvantage into a very efficient and speedy “sales call.”
What types of businesses does SEO work for?
Whether a business is new or old, big or small, struggling or successful, website optimization can bring about many benefits for any company as it can improve brand visibility and accessibility. If you want your target audience to find you online quickly, you need SEO. The earlier and longer you invest in SEO, the better payout you’ll get from it in return.
Credible, truthful, relevant, and engaging content could turn what would otherwise be a disadvantage into a very efficient and speedy “sales call.”
Is SEO dead?
SEO definitely isn’t dead. In fact, 61% of marketers say enhancing SEO and growing their organic presence is their top inbound marketing priority. However, it’s not the same as it used to be and things are constantly evolving. What’s working today might not work tomorrow. So, successful SEO strategies need to be flexible.
Credible, truthful, relevant, and engaging content could turn what would otherwise be a disadvantage into a very efficient and speedy “sales call.”
How much should I pay for SEO services?
SEO prices differ depending on the services you get. Depending on your business needs, you can avail of either individual services or package deals.
What are the four types of SEO?
The four types of SEO are on-page SEO, off-page SEO, technical SEO, and content SEO. There are more types, however, and recent digitalization has paved the way for local SEO, mobile SEO, and e-commerce SEO.
Do I need SEO for my website?
If you want results and organic growth, the answer is a definite yes! SEO helps make your website more visible online, meaning more people will see it compared to others that don’t utilize SEO services.
Is it worth paying for SEO agencies in the Philippines?
Paying in exchange for site traffic and potentially new customers is always a good idea! If you don’t believe in SEO, at least believe in its potential to usher in new clients and generate revenue for your brand. We are an affordable SEO company in the Philippines, get in touch to explore our package offerings.
Here to Learn?
We practice what we preach, building awesome SEO and organic marketing content to help you improve every aspect of your game. Here are our most recent articles:




